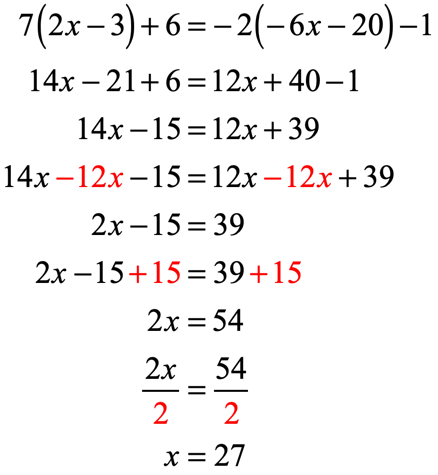The Distributive Property of Multiplication over Addition
The distributive property of multiplication over addition allows us to eliminate the grouping symbol, usually in the form of a parenthesis. The following diagram illustrates the basic pattern or formula how to apply it.
Basic “Formula” of the Distributive Property
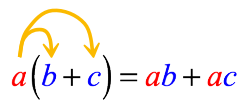
Few notes:
- This is done by taking the outer term and multiplying it by each term inside the parenthesis.
- Thus, take the term [latex]a[/latex] which is outside the parenthesis and distribute it into each term inside the parenthesis.
- Notice that [latex]ab[/latex] means [latex]a[/latex] times [latex]b[/latex].
- Similarly, [latex]ac[/latex] means [latex]a[/latex] times [latex]c[/latex].
Combining Like Terms using the Distributive Property
Example 1: Distribute then simplify the expression below.
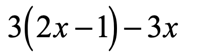
Is it possible to combine the [latex]x[/latex]-terms right away? Not so fast! The term [latex]2x[/latex] is inside the parenthesis, while [latex]3x[/latex] is outside. There is no way we can combine them because they are found in different locations.
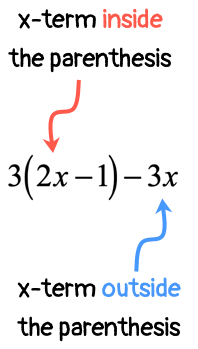
What we need to do is to first eliminate the parenthesis symbol before we can combine the like terms that would arise either by adding or subtracting. This is where the usefulness of this property comes into play.
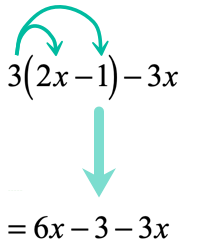
At this point, the parenthesis is gone and all [latex]x[/latex]-terms are free to be combined. I would rearrange them by placing similar terms side by side before performing the required operation.
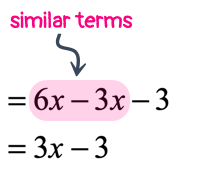
Example 2: Distribute then simplify the expression below.
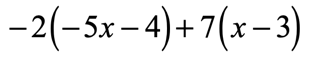
Since we have two parentheses here, we must apply the property twice. Doing that should get rid of the grouping symbols and allow us to combine like terms.
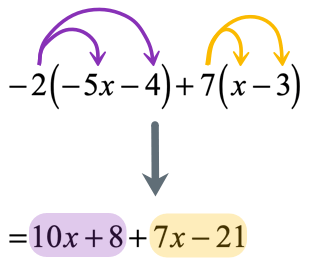
After eliminating the two parentheses, it is now possible to combine like terms. Make sure to rearrange the terms such that like terms are placed side by side before doing the required operation of addition or subtraction.
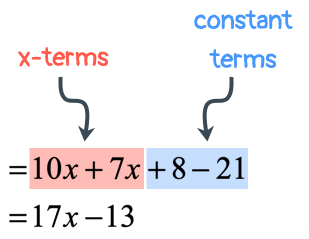
Example 3: Distribute then simplify the expression below.
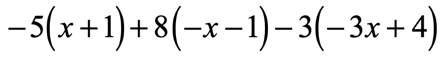
I hope that you can see the pattern now. By having three parentheses, we are required to apply it three times as well.
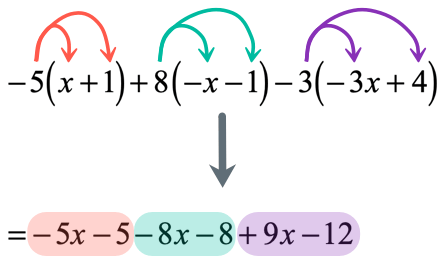
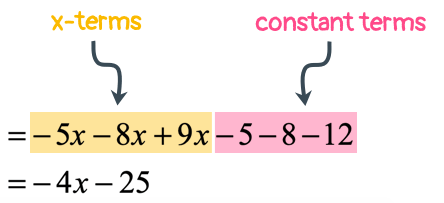
Since all the terms are outside the parenthesis now, go ahead combining the like terms.
Example 4: Distribute then simplify the expression below.
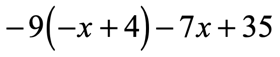
Solution:
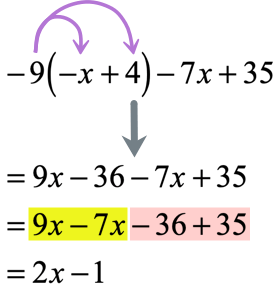
Example 5: Distribute then simplify the expression below.
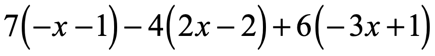
Solution:
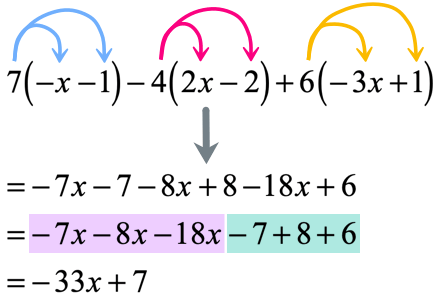
Example 6: Distribute then simplify the expression below.
![-2[3(2x-5)-2(-x-1)]](https://www.chilimath.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/01/distrprop-ex8a.png)
Solution:
Apply the distributive property to the inner parentheses first, and combine like terms. Finally, get rid of the square bracket symbol by distributing one more time.
![-2 = -2 = -2 = -2[8x-13] = -16x+26](https://www.chilimath.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/01/distprop-ex-8b.jpg)
You can also use the Distributive Property when you solve equations.
Solving Linear Equations using the Distributive Property
Example 7: Solve the linear equation below using the Distributive Property.
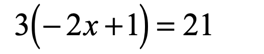
As you can see, the outer number [latex]3[/latex] found directly to the left of a parenthesis suggests that we can apply the property to eliminate the grouping symbol.
- Take that number [latex]3[/latex] and multiply to each term inside the parenthesis.
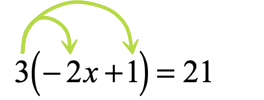
- After doing so, the parenthesis symbol should go away. Then we can proceed with the usual steps in solving the equation. For this example, we will isolate the variable “[latex]x[/latex] to the left of the equation. After the distribution, subtract both sides by [latex]3[/latex] and followed by the division of [latex] – \,6[/latex] on both sides of the equation to arrive at the final answer.
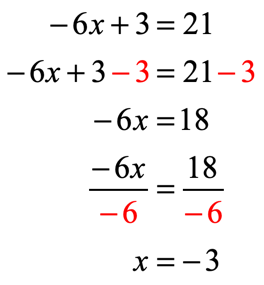
Example 8: Solve the linear equation below using the Distributive Property.
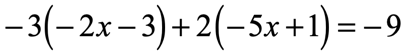
By having two parentheses on the left side of the equation, it implies that we have to distribute twice.
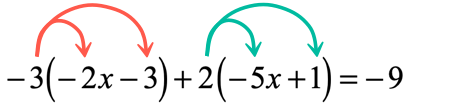
After getting rid of the grouping symbols, we can now combine like terms and isolate the variable on the left side of the equation.
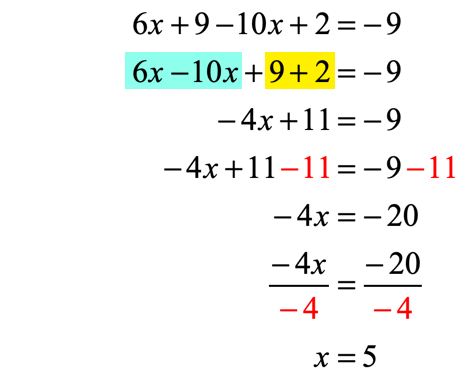
Example 9: Use the Distributive Property to solve the equation.
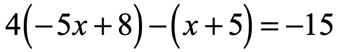
Solution:
Start by distributing [latex]4[/latex] into the first parenthesis followed by distributing [latex] – 1[/latex] into the second parenthesis. Next, combine similar terms that arise after eliminating the parentheses. Finally, solve [latex]x[/latex] by isolating it to the left side.
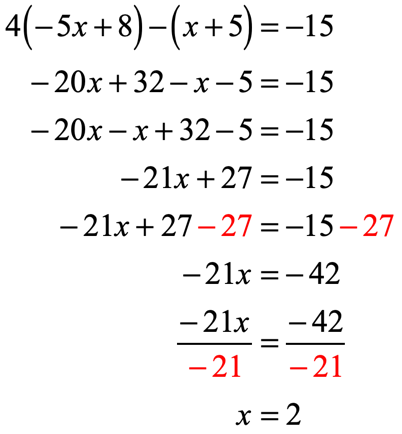
Example 10: Use the Distributive Property to solve the equation.
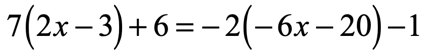
Solution:
Here we see two parentheses which means we will distribute twice, one on each side of the equation to eliminate the grouping symbols. Then solve the linear equation as usual.